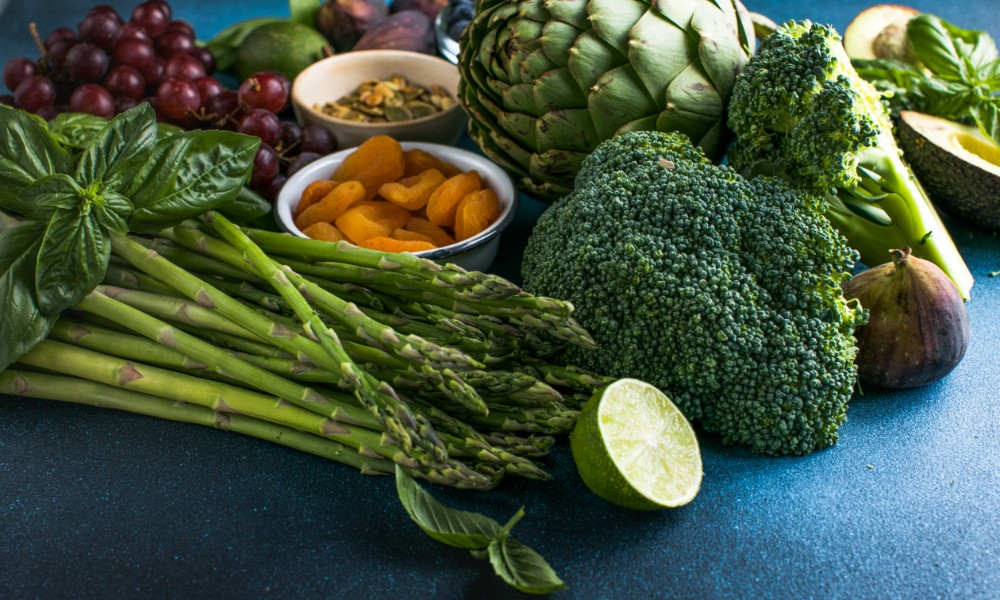
Lutein is a naturally occurring carotenoid found predominantly in green, leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale, as well as other foods like eggs and corn. Carotenoids are plant pigments that have powerful antioxidant properties and are responsible for the bright red, yellow, and orange colors in many fruits and vegetables.
The role of lutein in the body
Lutein’s function in the eyes
Lutein is vital for eye health, predominantly because it is concentrated in the macula, the part of the retina responsible for clear central vision. Lutein helps filter high-energy blue light, which can damage the delicate cells of the eyes, thereby reducing the risk of light-induced oxidative damage that can lead to macular degeneration (AMD).
The protective qualities of lutein contribute to its role in improving visual functions such as contrast sensitivity, reducing the effects of glare, and enhancing visual acuity in dim light or at night.
Antioxidant properties
Lutein is a powerful antioxidant, helping to combat free radical damage not just in the eyes, but throughout the body. By neutralizing these free radicals, lutein aids in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, processes linked to various chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
This protective effect is also important in the skin, where lutein helps to guard against UV and high-energy light damage, potentially reducing the risk of skin cancer and premature aging.
Lutein and brain health
Emerging research indicates that lutein is beneficial for brain health, particularly in aging populations. Lutein is believed to accumulate in the brain, where it likely performs the same antioxidant and light-filtering roles as it does in the eyes. Higher levels of lutein have been associated with improved cognitive function, memory retention, and efficiency in performing complex tasks in older adults, suggesting a protective effect against cognitive decline.
Sources of lutein
Dietary sources
Lutein is primarily found in green leafy vegetables, which are the most potent sources. Here are some of the best options:
- Spinach is one of the richest sources of lutein, with one cup of cooked spinach providing about 20 mg.
- Kale, like spinach, is an excellent source, offering around 23.8 mg per cup when cooked.
- Other vegetables such as broccoli, peas, and Brussels sprouts also contribute significant amounts of lutein.
Fruits, although not as rich in lutein as vegetables, can still contribute to lutein intake. Persimmons, kiwi, and grapes contain lutein in smaller amounts. Eggs, particularly the yolks, are another good source of lutein, making them an important dietary component for those who might not consume adequate amounts of leafy greens.
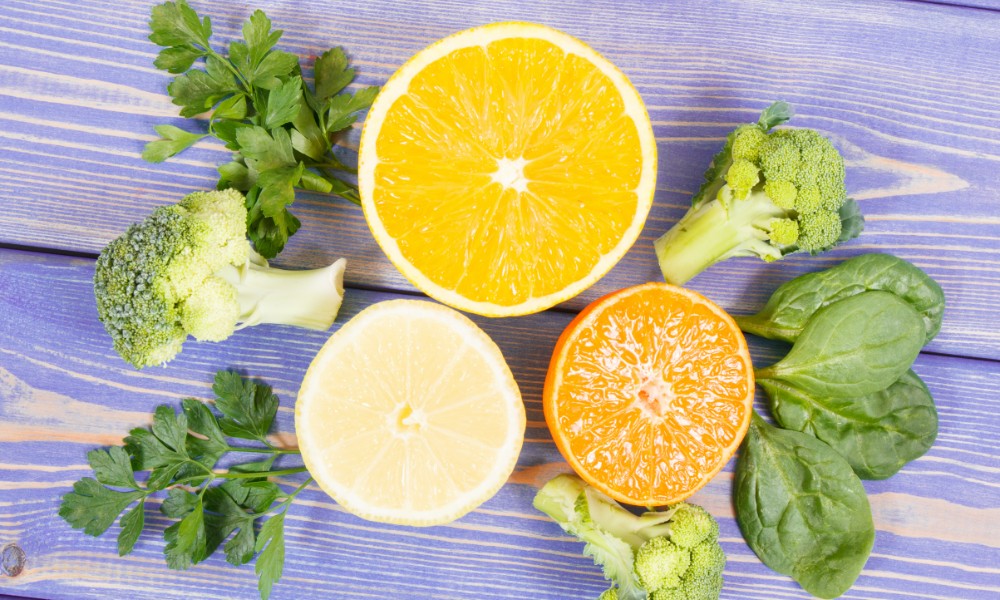

Absorption and bioavailability
The absorption of lutein from food sources can be influenced by several factors:
- Fat presence: Lutein is fat-soluble, meaning that its absorption is enhanced when consumed with dietary fats. Adding a little olive oil to a salad containing spinach or kale can help increase the amount of lutein your body absorbs.
- Food preparation: Cooking can help break down the cell walls of plants, making lutein more available. Light steaming of vegetables like spinach and kale is effective in increasing their lutein bioavailability.
- Food matrix: The complexity of the food matrix and how lutein is incorporated within it also affect its bioavailability. For instance, lutein is more readily available from egg yolks than from leafy vegetables due to different matrices, even though the concentration in vegetables is higher.
Benefits of lutein for eye health
Protection against age-related macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss among older adults.
The macula, where lutein is concentrated, is crucial for clear central vision. Lutein helps protect this area by filtering harmful blue light and mitigating oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
Several epidemiological studies and clinical trials have demonstrated that higher dietary intake of lutein is associated with a reduced risk of developing advanced AMD. Moreover, lutein may slow the progression of AMD in individuals already diagnosed by enhancing the density of the macular pigment that acts as a natural sunscreen for the eyes.
Impact on cataracts
Cataracts develop when proteins in the eye’s lens clump together, clouding the lens and leading to blurred vision. Antioxidants like lutein can help prevent these proteins from oxidizing, thus reducing the risk and delaying the progression of cataracts.
Studies have shown that individuals with a higher intake of lutein and zeaxanthin have a lower risk of developing significant cataract formation, highlighting the importance of a lutein-rich diet for maintaining lens clarity and overall eye health.
Enhanced visual function
Lutein not only protects against eye diseases but also contributes to functional benefits in vision. These include improved contrast sensitivity, which helps individuals distinguish objects from their background, and better glare recovery, which is crucial for night driving.
Additionally, lutein may help improve visual acuity in low-light and high-glare situations, further supporting its role in maintaining visual performance as we age.
Lutein and overall health
Cardiovascular health
The antioxidant properties of lutein extend to protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation, two significant factors in the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Lutein has been found to inhibit the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, a key step in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Regular intake of lutein-rich foods can therefore help maintain arterial health and reduce the risk of heart diseases, such as heart attacks and strokes.
Skin health
Lutein’s ability to filter high-energy wavelengths of light helps protect the skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation, which can lead to premature aging and skin cancer. Dietary lutein accumulates in the skin, where it enhances its antioxidant capacity and may improve skin hydration, elasticity, and lipid content, contributing to better skin health and appearance.
Cognitive function
Emerging research has linked lutein to improvements in cognitive function, especially in older adults. Lutein is thought to accumulate in the brain, where it protects neuronal integrity and function through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Higher levels of lutein are associated with enhanced memory, faster cognitive processing speeds, and better verbal fluency. These findings suggest that lutein may play a crucial role in preventing the decline in cognitive functions associated with aging and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
The impact of lutein on visual development in children
Importance of lutein in early life
Lutein’s role in eye health is not limited to the prevention and management of age-related conditions; it also plays a critical role in visual development during childhood.
Lutein is one of the predominant carotenoids found in the retina, and it begins to accumulate in the eyes from infancy. Adequate intake of lutein during these formative years can support proper vision development and contribute to the density of the macular pigment, which is essential for protecting the eyes against blue light and oxidative damage.
Dietary sources and recommendations for children
Ensuring that children receive sufficient lutein involves incorporating lutein-rich foods into their diet from an early age. Foods such as spinach, kale, and other green leafy vegetables, as well as eggs, provide accessible sources of lutein that can be easily added to a child’s diet.
Pediatric health experts suggest that encouraging a diet with diverse fruits and vegetables can help establish healthy eating habits that include adequate levels of important nutrients like lutein.
Lutein’s role in athletic performance
Visual benefits for athletes
Athletes may benefit particularly from lutein’s ability to enhance visual function. Sports performance often depends on optimal visual capabilities, including sharp vision, good contrast sensitivity, and effective glare reduction—traits that lutein helps improve. Studies have indicated that athletes with higher dietary intake of lutein exhibit better visual reaction times and hand-eye coordination, attributes that are crucial in many sports.

Antioxidant effects in athletic health
In addition to its visual benefits, lutein’s antioxidant properties play a role in general physical health and recovery. For athletes, managing oxidative stress and inflammation is crucial, as these can result from intense physical activity and can impact muscle recovery and performance. Integrating lutein-rich foods into an athlete’s diet may help enhance recovery times, reduce muscle damage, and improve overall physical health by mitigating oxidative stress and supporting cellular health in muscles.
Lutein and its influence on metabolic health
Connection between lutein and metabolic syndrome
Recent studies are beginning to explore the relationship between lutein and metabolic health, particularly in the context of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
Lutein’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may play a role in improving metabolic markers, helping to reduce the risk factors associated with metabolic syndrome.
Lutein’s potential effects on insulin sensitivity and obesity
Research suggests that lutein may influence insulin sensitivity and fat metabolism, which are critical aspects of metabolic health. In animal studies, lutein supplementation has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, which are both beneficial in managing or preventing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, there is emerging evidence that lutein may help regulate adipose tissue function and fat metabolism, potentially aiding in weight management and reducing the risk factors for obesity-related complications.
Dietary strategies to enhance metabolic health through lutein
Incorporating lutein-rich foods into the diet can be a strategic part of managing or preventing metabolic syndrome. Since lutein is fat-soluble, consuming foods rich in healthy fats such as avocados or nuts along with lutein-rich vegetables can enhance its absorption, maximizing its metabolic benefits. Regular consumption of a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that include lutein sources—like kale, spinach, and broccoli—can contribute to improved overall metabolic health.
Recommended intake of lutein
Establishing a recommended intake
Although there is no formally established Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for lutein, various health organizations and nutritional studies suggest a range of intake that might offer significant health benefits. Research generally supports a daily intake of 6 to 10 milligrams of lutein to help reduce the risk of chronic eye diseases and possibly other health conditions. These recommendations are based on observational studies and clinical trials that have linked these levels of intake with lower rates of age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
Factors influencing lutein needs
Individual dietary requirements for lutein can vary based on several factors, including age, genetic predispositions, and overall health status, particularly of the eyes and cardiovascular system. For example, individuals with a family history of AMD or who are at higher risk of oxidative stress might benefit from the higher end of the recommended intake spectrum. Furthermore, lifestyle factors, such as exposure to sunlight and dietary habits, can also influence lutein needs.

Supplementation and safety
For individuals who find it challenging to achieve the recommended intake of lutein through diet alone – perhaps due to dietary restrictions or preferences—supplements can be a viable option.
Lutein supplements are often combined with zeaxanthin, another carotenoid, enhancing their beneficial effects on eye health.
Safety profile of lutein supplements
Lutein supplements are generally considered safe when taken at recommended levels. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for those who are pregnant, nursing, or have a chronic health condition.
While adverse effects are rare, consuming lutein in extremely high doses over long periods could potentially lead to an imbalance in carotenoid levels, which might affect skin coloration, turning it slightly yellowish, a harmless condition known as carotenemia.

Lutein research: past and future
Historical insights
Lutein research has significantly evolved over the past few decades. Initially focused on the role of lutein in eye health, particularly in the prevention and management of AMD and cataracts, early studies provided foundational knowledge about the absorption and biological effects of lutein. These studies have established lutein as crucial in dietary strategies for maintaining eye health and preventing the progression of age-related visual decline.
Emerging areas and future directions
The future of lutein research is expanding into new and exciting territories. Ongoing studies are exploring the impact of lutein on cognitive functions, examining how it may protect against the cognitive decline associated with aging and possibly neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Furthermore, researchers are investigating the broader systemic effects of lutein on skin health, cancer prevention, and overall oxidative stress.
Research into the bioavailability of lutein from different dietary sources and the synergistic effects of lutein with other nutrients is also gaining interest. This could lead to improved dietary guidelines and supplement formulations that optimize the absorption and efficacy of lutein.
The last word on lutein and eye health
In conclusion, lutein is a critical nutrient for maintaining eye health and overall well-being. Its benefits extend beyond just vision protection, influencing everything from skin health to cardiovascular function. Regular consumption of lutein-rich foods can significantly contribute to long-term health and vitality, underscoring the importance of a balanced and colorful diet.




